Cardiology
What are stress test?
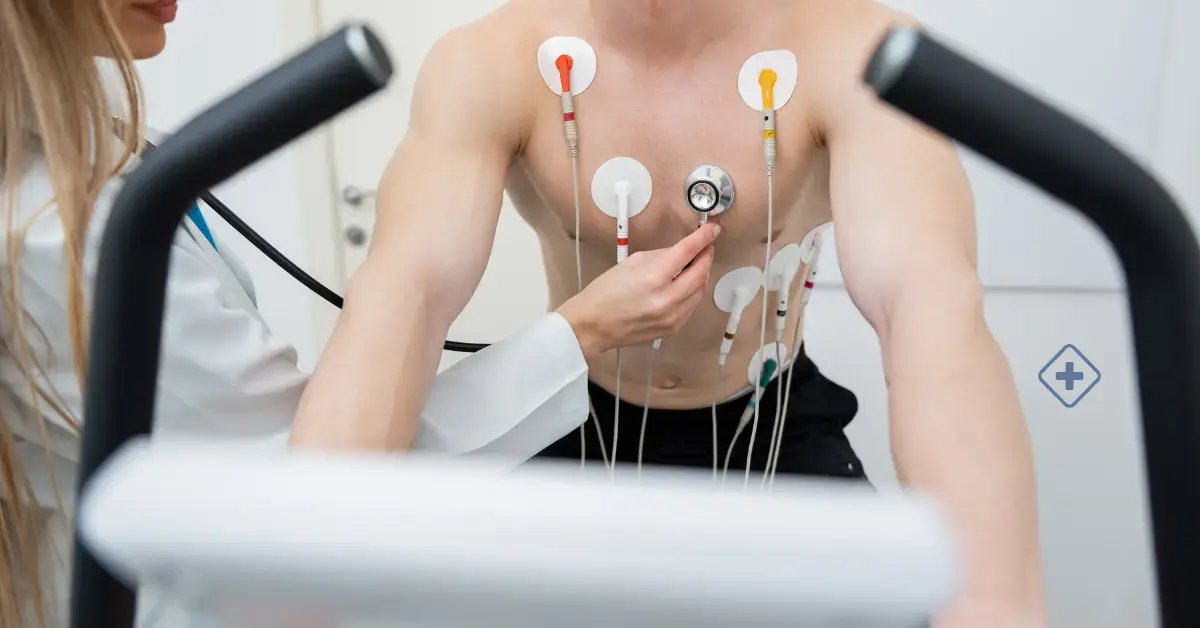
The stress test examines how the heart works during physical activity.
What are stress test?
Stress test allow us to see how the heart responds to physical activity. For example, when we exercise, the heart pumps faster and harder. Certain heart conditions are more easily detected when the heart is working.
For example, in a stress test, your heart function is tested while exercising on a treadmill or stationary bike.If you cannot do this for health reasons, you will be given medication that makes your heart beat faster and stronger as if you were exercising. If you cannot complete the stress test within a certain period, this could mean that the blood flow to the heart has been reduced. Some heart conditions could cause this.
What are they used for?
Stress tests are used to detect certain diseases such as:
You may need a stress test if you have symptoms of reduced blood flow to the heart. Some of the symptoms are:
What happens during a stress test?
There are three main stress tests: exercise stress test, nuclear stress test, and stress echocardiography. Any of these can be done in a doctor's office, outpatient clinic, or hospital.
Exercise stress test:
Wear comfortable shoes and loose clothing to make exercising easier. You may be asked not to eat or drink for several hours before the test. If you have questions about how to prepare, ask our Cardiology specialist.
Are there any risks in this test?
Stress tests are safe in most cases. However, sometimes exercise or medicine that increases the heart rate can cause dizziness, chest pain, or nausea.
During the test, you will have the specialist's full attention to reduce the risk of complications or quickly treat any problems that may occur.
The radioactive contrast material used in the nuclear stress test is safe for most people. However, in rare cases, it can cause an allergic reaction.
The nuclear stress test is not recommended for pregnant women as the contrast material could be dangerous to the fetus.
What do the results mean?
No problems with blood flow are found in a typical result. However, if the result is not normal, it may mean a decrease in the blood flow to the heart. We group some of the reasons:
If you have questions about your results, visit your Cardiology specialist.
Meet the doctors at BlueNetHospitals and schedule a Cardiology appointment.
BlueNetHospitals - Hospital Los Cabos
BlueNet Hospitals
Stress test allow us to see how the heart responds to physical activity. For example, when we exercise, the heart pumps faster and harder. Certain heart conditions are more easily detected when the heart is working.
For example, in a stress test, your heart function is tested while exercising on a treadmill or stationary bike.If you cannot do this for health reasons, you will be given medication that makes your heart beat faster and stronger as if you were exercising. If you cannot complete the stress test within a certain period, this could mean that the blood flow to the heart has been reduced. Some heart conditions could cause this.
What are they used for?
Stress tests are used to detect certain diseases such as:
- Coronary artery disease, which can cause dangerous blockages in blood flow to the heart
- Detect an arrhythmia, which causes the heart to beat irregularly
- Know what level of exercise is safe for you
- Determine the effectiveness of the treatment if you have already been diagnosed with heart disease
- Determine if you are at risk for a heart attack or other severe heart disease
You may need a stress test if you have symptoms of reduced blood flow to the heart. Some of the symptoms are:
- Angina, caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart
- Trouble breathing
- Fast heartbeat
- Arrhythmia, irregular heartbeat
- You are going to start an exercise program
- You recently had heart surgery
- You are being treated for heart disease
- You have suffered a heart attack
- You have diabetes, a family history of heart problems, or heart disease
What happens during a stress test?
There are three main stress tests: exercise stress test, nuclear stress test, and stress echocardiography. Any of these can be done in a doctor's office, outpatient clinic, or hospital.
Exercise stress test:
- The specialist places several electrodes on you; they are small sensors that adhere to the skin, arms, legs, and chest. Before doing this, you may need to shave off excess hair
- Wires connect the electrodes to an electrocardiography (ECG) machine, which records the heart's electrical activity
- Then you start strolling on a treadmill or stationary bike
- Little by little, you start walking or pedaling faster, and the incline and resistance increase
- You continue walking or pedaling until you reach a target heart rate (number of beats per minute) set by your doctor. If you have chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, or dizziness, you may need to stop earlier. The test could also be prevented if the EKG indicates that you are having a heart problem
- Once the test is finished, the specialist will monitor you for 10 to 15 minutes or until your heart rate returns to normal
- The nuclear stress test and stress echocardiography are tests that capture images of the heart while you exercise
- You will lie on a stretcher
- The specialist will insert an IV into your arm. An IV is put in that contains radioactive contrast material. This material allows the specialist to see images of the heart. It takes 15 to 40 minutes for the heart to absorb the radioactive contrast material
- A special camera takes pictures of the heart at rest
- The rest of the study is similar to an exercise stress test
- You will be hooked up to an EKG machine and then walk on a treadmill or pedal an exercise bike
- If your health does not allow you to do this, you will be given a medicine that makes your heart beat faster and stronger
- When your heart is working at its best, you will receive another injection with radioactive contrast material
- You will need to wait 15 to 40 minutes for the heart to absorb the contrast material
- Then you will exercise again, and the special camera will capture more images of your heart
- The specialist will compare the two groups of images of the heart at rest and straining
- After the test, your healthcare professional will monitor you for 10–15 minutes or until your heart rate returns to normal
- The radioactive contrast material will pass out of your body naturally through the urine. Drinking lots of water will help you eliminate it faster
- You lie on a stretcher
- The specialist will rub a special gel on a wand-like device called a transducer. They will then place the transducer on your chest
- This device generates sound waves that create films of the heart
- After taking these images, you will exercise on a treadmill or stationary bike like other types of stress tests
- If your health does not allow you to do this, you will be given a medicine that makes your heart beat faster and stronger
- Then more images will be taken when the heart rate increases or the heart is making the maximum effort
- The specialist will compare the two groups of images, of the heart at rest and straining
- After the test, your healthcare professional will monitor you for 10–15 minutes or until your heart rate returns to normal
Wear comfortable shoes and loose clothing to make exercising easier. You may be asked not to eat or drink for several hours before the test. If you have questions about how to prepare, ask our Cardiology specialist.
Are there any risks in this test?
Stress tests are safe in most cases. However, sometimes exercise or medicine that increases the heart rate can cause dizziness, chest pain, or nausea.
During the test, you will have the specialist's full attention to reduce the risk of complications or quickly treat any problems that may occur.
The radioactive contrast material used in the nuclear stress test is safe for most people. However, in rare cases, it can cause an allergic reaction.
The nuclear stress test is not recommended for pregnant women as the contrast material could be dangerous to the fetus.
What do the results mean?
No problems with blood flow are found in a typical result. However, if the result is not normal, it may mean a decrease in the blood flow to the heart. We group some of the reasons:
- Having coronary artery disease
- Having a scar from a previous heart attack
- Undergoing heart treatment that is not working
- Being in poor physical condition
If you have questions about your results, visit your Cardiology specialist.
Meet the doctors at BlueNetHospitals and schedule a Cardiology appointment.
BlueNetHospitals - Hospital Los Cabos
BlueNet Hospitals
Trending Topics
Cardiology
Trending Topics
Septoplasty
Septoplasty is a highly effective procedure for correcting a deviated septum
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes chronic inflammation.
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA)
The level of PSA in the blood can provide valuable information about prostate health.
Emphysema
Emphysema symptoms can be subtle at first but tend to worsen over time.
Health Library
Cardiology
Learn More About:
- Do You Need an Appointment with a Specialist?
- call us
- write us
- let's talk




.webp?q=G8yS1LuiXvQWpwEE)

.webp?q=3kPxXZSeQp7cWCSo)