Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia is the increase in the production of cells in a healthy organ or tissue.

Hyperplasia is the increase in the production of cells in a healthy organ or tissue; it can be physiological or pathological.
Physiological hyperplasia is harmless; it can occur at a specific point in life, such as in some cases of pregnancy. It can be hormonal or as a result of increased secretion of any hormone. It is classified in:
-
Hormonal hyperplasia increases the functional capacity of a tissue that requires it
-
Endometrial hyperplasia, the endometrium (uterine lining) is abnormal
-
Compensatory hyperplasia increases the mass of tissues after injury
Pathological hyperplasia can occur due to excessive hormonal stimulation or other effector cell growth factors. This condition can be linked to diseases such as cancer.
Among the pathological hyperplasia are:
-
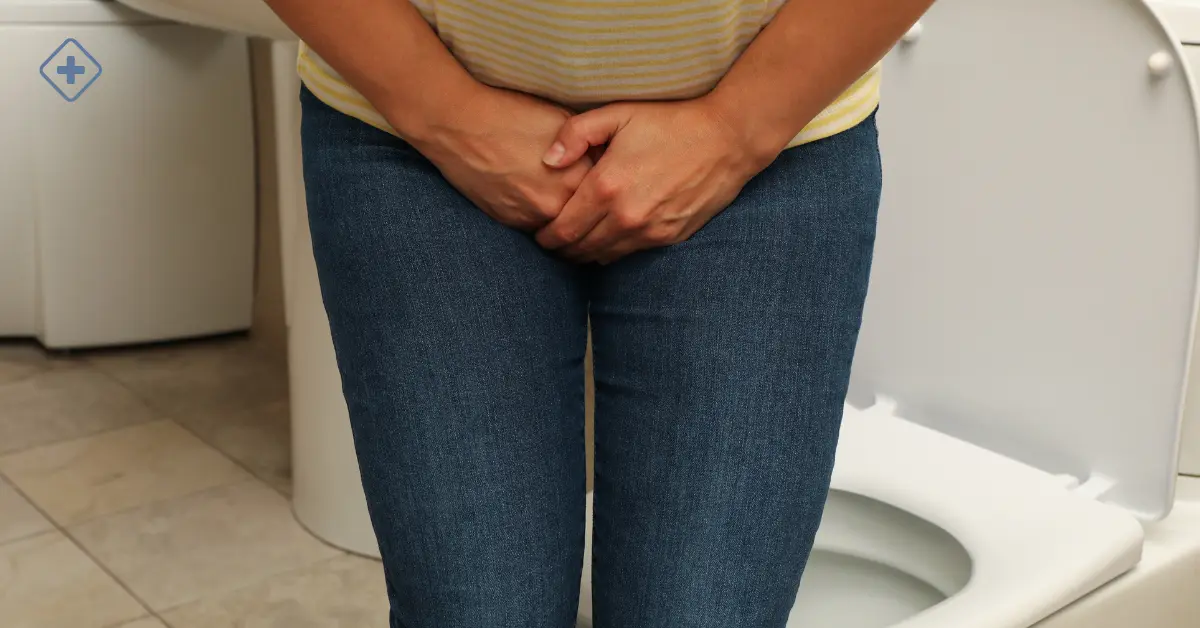
Benign prostatic hyperplasia(BPH), also known as an enlarged prostate gland, occurs more frequently during aging men. It can lead to urinary problems, such as blocked urine flow from the bladder, bladder, urinary tract, or kidney problems
Causes of Hyperplastia
Viral infections are the main cause of hyperplasia.
Symptoms of Hyperplastia
Symptoms vary depending on the type of hyperplasia.
Symptoms of Benign prostatic hyperplasia
-
Trouble starting to urinate
-
Weak or slow urine flow
-
Dribbling after urination
-
Problems emptying the bladder completely
-
Blood in the urine
Symptoms of Endometrial hyperplasia
-
Abnormal menstrual bleeding
-
Bleeding or spotting between menstrual periods
-
Missed menstrual period
-
Uterine bleeding after menopause
Risk factors of Hyperplastia
-
Age, after aging, enlargement of the prostate gland is more common
-
Family background
-
Diabetes and heart disease
-
Lifestyle
Diagnosis of a Hyperplasia
The doctor will perform physical exams, questions related to your symptoms, lifestyle, and medical history. Doctors specializing in treating hyperplasia are the Urologist or Gynecologist, depending on the type of this.
Following are the most common tests to perform to diagnose hyperplasia.
The Urologist may perform the following tests to detect benign prostatic hyperplasia:
-
Prostate-specific antigen
-
Biopsy
-
Cystoscopy
-
Urinary flow test
The Gynecologist may perform the following tests to detect endometrial hyperplasia:
Analysis of a sample of cells
-
Biopsy
Treatment of a Hyperplasia
Treatment varies depending on the type of hyperplasia that is present and the severity of it.
Common treatment options include:
-
Hormonal injections
-
Surgical interventions
-
Go to periodic reviews
The Urologist or Gynecologist will help you decide which treatment is best for your health.
Living with Hyperplasia
When you have already been diagnosed with Hyperplasia, follow the treatment provided by your Urologist or Gynecologist.
Some things to consider that could help improve the quality of life are:
-
Follow a healthy diet
-
Attend your regular review appointments
-
Reduce stress
-
Don't use drugs or alcohol
-
Don't smoke
-
Take the medications provided by your doctor
When do you have to see a doctor?
Make your appointment with the doctor in case of presenting some of the symptoms mentioned or in case of detecting another abnormal symptom.
The Urologist is in charge of treating benign prostatic hyperplasia; The Gynecologist treats cases of endometrial hyperplasia, both will be in charge of making a diagnosis to identify the cause of the symptoms and identify the severity of the condition.
At the time of your appointment, keep a list of your symptoms, duration, and what you think triggered them. Also, mention any medications you are taking.
BlueNetHospitals - Hospital Los Cabos
BlueNet Hospitals.
Health Library
Urology

Urinary Incontinence
The treatment of urinary incontinence varies depending on the type and severity of symptoms
Understanding Andropause: A Complete Guide
Andropause is primarily the result of a decrease in testosterone production
Male Infertility
Infertility occurs due to reduced sperm production, abnormal sperm function, or blockage that prevents sperm release.
Ureteroscopy
Before, During & After
- Do You Need an Appointment with a Specialist?
- call us
- write us
- let's talk